Stainless Steel Plate
A Corrosion Resistant Austenitic Stainless Steel with a High Molybdenum and Nitrogen Content Developed for Use in Chloride Containing Environments.
Available thicknesses for Alloy 317LMN:
| 3/16" | 5/16" | 3/8" | 1/2" | 5/8" | 3/4" | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.8mm | 7.9mm | 9.5mm | 12.7mm | 15.9mm | 19mm | ||
Alloy 317LMN (UNS S31726) is an austenitic chromium-nickel-molybdenum stainless steel with corrosion resistance superior to 316L and 317L. The higher molybdenum content, combined with an addition of nitrogen, provides the alloy with its enhanced corrosion resistance, especially in acidic chloride containing service. The combination of molybdenum and nitrogen also improves the alloys resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
The nitrogen content of Alloy 317LMN acts as a strengthening agent giving it a higher yield strength than 317L .Alloy 317LMN is also a low carbon grade which enables it to be used in the as-welded condition free from chromium carbide precipitation on the grain boundaries.
Alloy 317LMN is non-magnetic in the annealed condition. It cannot be hardened by heat treatment, only by cold working. The alloy can be easily welded and processed by standard shop fabrication practices.
Specification Sheet Overview
for Alloy 317LMN (UNS S31726)
W. Nr. 1.4439:

Applications
- Air Pollution Control—flue gas desulfurization systems, stack liners, absorbers, ducts, dampers, and fans
- Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
- Food and Beverage Processing
- Pharmaceutical Equipment
Standards
ASTM........A 240ASME........SA 240
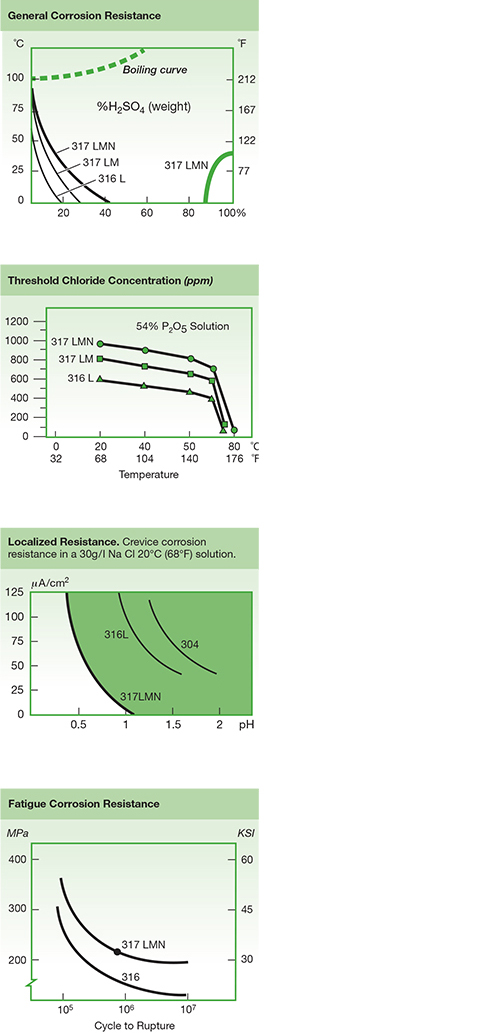
Corrosion Resistance
The higher molybdenum and nitrogen content of Alloy 317LMN assures superior general and localized corrosion resistance in most media when compared with 304/304L, 316/316L and even 317L stainless steels. Environments that don’t attack 304/304L stainless steel will normally not corrode 317LMN. One exception, however, are strongly oxidizing acids such as nitric acid. Alloys that contain molybdenum generally do not perform as well in these environments.
Alloy 317LMN has excellent corrosion resistance in a wide range of chemicals. It resists attack in sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, acidic chlorine and phosphoric acid. It is used in handling hot organic and fatty acids often present in food and pharmaceutical processing applications.
Because of its low carbon content, Alloy 317LMN should be utilized when it will be exposed to temperatures in the chromium carbide precipitation range of 800-1500°F (427-816°C). The higher nitrogen content of 317LMN further retards the precipitation of sigma phase as well as carbides.
In general, austenitic stainless steels are subject to chloride stress corrosion cracking in halide service. Although 317LMN is somewhat more resistant to stress corrosion cracking than 304/304L stainless steels, because of its higher molybdenum content, it is still susceptible.
The higher chromium, molybdenum and nitrogen content of 317LMN enhance its ability to resist pitting and crevice corrosion in the presence of chlorides and other halides. The Pitting Resistance Equivalent including Nitrogen number (PREN) is a relative measure of pitting resistance. The following chart offers a comparison Alloy 317LMN and other austenitic stainless steels.
| ALLOY | PRE | ALLOY | PRE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | 25 | 317LMN | 38 |
| 317L | 30 | SSC-6MO | 48 |
| 317LM | 34 | 625 | 52 |
| 904L | 36 | 276 | 69 |
PRE = Cr + 3.3Mo + 30N
Chemical Analysis
Weight % (all values are maximum unless a range is otherwise indicated)
| Chromium | 17.0 min.-20.0 max. | Manganese | 2.00 |
| Nickel | 13.5 min.-17.5 max. | Phosphorus | 0.045 |
| Molybdenum | 4.0 min.-5.0 max. | Sulfur | 0.030 |
| Nitrogen | 0.10 min.-0.20 max. | Silicon | 0.75 |
| Carbon | 0.030 | Iron | Balance |
Physical Properties
Density
0.290 lbs/in38.0 g/cm3
Specific Heat
0.12 BTU/lb-°F (32 – 212°F)502 J/kg-°K (0 – 100°C)
Modulus of Elasticity
29.0 x 106 psi200 GPa
Thermal Conductivity 212°F (100°C)
8.7 BTU/hr/ft2/ft/°F1.26 W/m-°K
Melting Range
2540 – 2630°F1393 – 1443°C
Electrical Resistivity
33.5 Microhm-in at 68°C85.1 Microhm-cm at 20°C
| Temperature Range | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| °F | °C | in/in °F | cm/cm °C |
| 68-212 | 20-100 | 8.9 x 10-6 | 16.03 x 10-6 |
Mechanical Properties
Typical Values at 68°F (20°C)
| Yield Strength 0.2% Offset |
Ultimate Tensile Strength |
Elongation in 2 in. |
Hardness | Reduction in Area |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| psi (min.) | (MPa) | psi (min.) | (MPa) | % (min.) | (max.) | % |
| 35,000 | 205 | 80,000 | 550 | 40 | 96 Rockwell B | 69 |
Fabrication Data
Alloy 317LMN can be easily welded and processed by standard shop fabrication practices.
Cold Forming
The cold formability of Alloy 303 is adversely impacted by the high sulfur content. The alloy may be bent with a generous bend radius, however, when cold forming is required, 304 should be utilized.
Hot Forming
The alloy is quite ductile and forms easily. The addition of molybdenum and nitrogen implies more powerful processing equipment may be necessary when compared with the standard 304/304L grades.
Machining
The cold work hardening rate of Alloy 317LMN makes it less machinable than 410 stainless steel. The table below provides relevant machining data.
| Operation | Tool | Lubrication | CONDITIONS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth-mm | Depth-in | Feed-mm/t | Feed-in/t | Speed-m/min | Speed-ft/min | |||
| Turning | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 6 | .23 | 0.5 | .019 | 11-16 | 36-52 |
| Turning | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 3 | .11 | 0.4 | .016 | 18-23 | 59-75 |
| Turning | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 1 | .04 | 0.2 | .008 | 25-30 | 82-98 |
| Turning | Carbide | Dry or Cutting Oil | 6 | .23 | 0.5 | .019 | 70-80 | 230-262 |
| Turning | Carbide | Dry or Cutting Oil | 3 | .11 | 0.4 | .016 | 85-95 | 279-313 |
| Turning | Carbide | Dry or Cutting Oil | 1 | .04 | 0.2 | .008 | 100-110 | 328-361 |
| Depth of cut-mm | Depth of cut-in | Feed-mm/t | Feed-in/t | Speed-m/min | Speed-ft/min | |||
| Cutting | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 1.5 | .06 | 0.03-0.05 | .0012-.0020 | 16-21 | 52-69 |
| Cutting | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 3 | .11 | 0.04-0.06 | .0016-.0024 | 17-22 | 56-72 |
| Cutting | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 6 | .23 | 0.05-0.07 | .0020-.0027 | 18-23 | 59-75 |
| Drill ø mm | Drill ø in | Feed-mm/t | Feed-in/t | Speed-m/min | Speed-ft/min | |||
| Drilling | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 1.5 | .06 | 0.02-0.03 | .0007-.0012 | 10-14 | 33-46 |
| Drilling | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 3 | .11 | 0.05-0.06 | .0020-.0024 | 12-16 | 39-52 |
| Drilling | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 6 | .23 | 0.08-0.09 | .0031-.0035 | 12-16 | 39-52 |
| Drilling | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 12 | .48 | 0.09-0.10 | .0035-.0039 | 12-16 | 39-52 |
| Feed-mm/t | Feed-in/t | Speed-m/min | Speed-ft/min | |||||
| Milling Profiling | High Speed Steel | Cutting Oil | 0.05-0.10 | .002-.004 | 10-20 | 33-66 | ||
Welding
Alloy 317LMN can be readily welded by most standard processes including TIG/GTAW, MIG/GMAW, MMAW and SAW. A post weld heat treatment is not necessary.
NOTE: The information and data in this product data sheet are accurate to the best of our knowledge and belief, but are intended for informational purposes only, and may be revised at any time without notice. Applications suggested for the materials are described only to help readers make their own evaluations and decisions, and are neither guarantees nor to be construed as express or implied warranties of suitability for these or other applications. Stainless Steel, Nickel Alloy and Titanium products are classified as sheet if the thickness of the metals is less than 3/16” (4.7mm). If the thickness of the metal is 3/16” (4.7mm) or more, then it is considered a plate.